Copernicus at a glance
Copernicus is the Earth observation component of the European Union’s Space programme, looking at our planet and its environment to benefit all European citizens. It offers information services that draw from satellite Earth Observation and in-situ (non-space) data.
The information provided by the Copernicus services can be used by end users for a wide range of applications in a variety of areas. These include urban area management, sustainable development and nature protection, regional and local planning, agriculture, forestry and fisheries, health, civil protection, infrastructure, transport and mobility, as well as tourism.
What is Earth Observation?
Earth Observation (EO) refers to the use of remote sensing technologies to monitor land, marine (seas, rivers, lakes) and atmosphere. Satellite-based EO relies on the use of satellite-mounted payloads to gather imaging data about the Earth’s characteristics. The images are then processed and analysed in order to extract different types of information that can serve a very wide range of applications and industries.
What is the role of Copernicus?
Copernicus is the Earth observation component of the European Union’s Space programme, looking at our planet and its environment to benefit all European citizens. It offers information services that draw from satellite Earth Observation and in-situ (non-space) data.
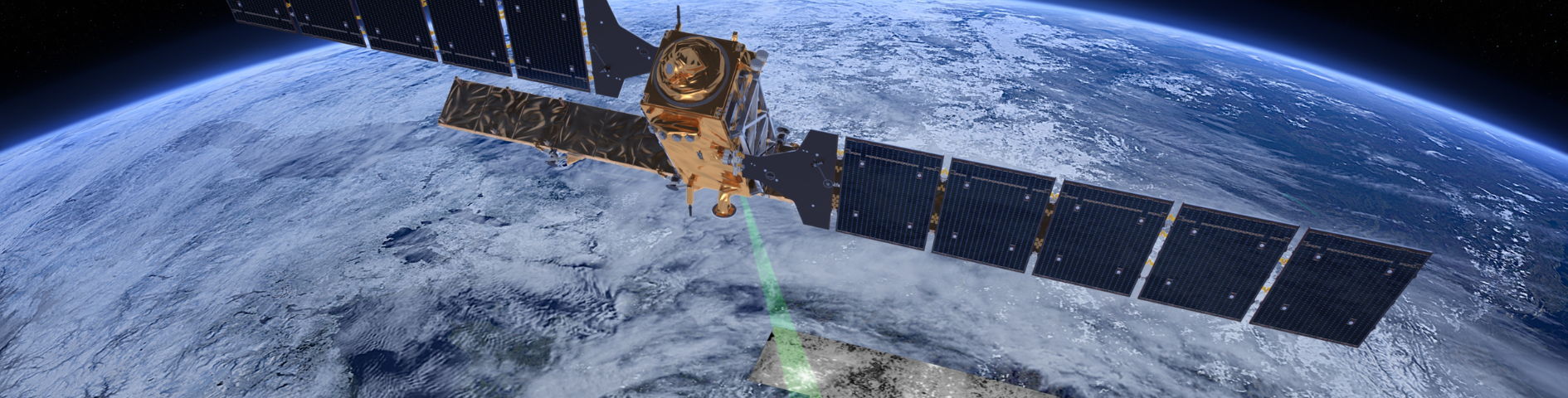
Copernicus is served by a set of dedicated satellites (the Sentinel families) and contributing missions (existing commercial and public satellites). The Sentinel satellites are specifically designed to meet the needs of the Copernicus services and their users. Since the launch of Sentinel-1A in 2014, the European Union set in motion a process to place a constellation of almost 20 more satellites in orbit before 2030.
Copernicus also collects information from in situ systems such as ground stations, which deliver data acquired by a multitude of sensors on the ground, at sea or in the air.
What services does Copernicus provide?
The provision of Copernicus services is based on the processing of environmental data collected from Earth observation satellites and in situ sensors. The Earth observation satellites which provide the data exploited by the Copernicus services are split into two groups of missions:
The Sentinels, which are developed for the specific needs of the Copernicus programme. Sentinel-1, -2, -3 and -6 are dedicated satellites, while Sentinel-4 and -5 are instruments onboard EUMETSAT’s weather satellites.
The Contributing Missions, which are operated by National, European or International organisations and already provide a wealth of data for Copernicus services.
The Copernicus services transform this wealth of satellite and in situ data into value-added information by processing and analysing the data.
These value-adding activities are streamlined through six thematic streams of Copernicus services:
The Copernicus services transform this wealth of satellite and in situ data into value-added information by processing and analysing the data. Datasets stretching back for years and decades are made comparable and searchable, thus ensuring the monitoring of changes; patterns are examined and used to create better forecasts, for example, of the ocean and the atmosphere. Maps are created from imagery, features and anomalies are identified and statistical information is extracted.
These value-adding activities are streamlined through six thematic streams of Copernicus services:
Use cases
The information provided by the Copernicus services can be used by end users for a wide range of applications in a variety of areas. These include urban area management, sustainable development and nature protection, regional and local planning, agriculture, forestry and fisheries, health, civil protection, infrastructure, transport and mobility, as well as tourism.
The main users of Copernicus services are policymakers and public authorities who need the information to develop environmental legislation and policies or to take critical decisions in the event of an emergency, such as a natural disaster or a humanitarian crisis.
Based on the Copernicus services and on the data collected through the Sentinels and the contributing missions, many value-added services can be tailored to specific public or commercial needs, resulting in new business opportunities.
Agriculture
Agriculture is one of the most promising applications in terms of the impact of Copernicus, especially in precision farming. Copernicus helps assess agricultural land use and trends, crop conditions and yield forecasts. It also supports input management, farm management recording and irrigation management. Together with Galileo and EGNOS, Copernicus is an essential technology for precision farming.
Blue Economy
Thanks to its capacity to monitor the physical and biogeochemical characteristics of the global ocean and regional seas, Copernicus supports a wide variety of Blue Economy applications such as the assessment of water quality, the mapping of fishing zones or the monitoring of harmful algal blooms.
Climate Change and Environment
By providing key indicators on climate change drivers such as carbon dioxide levels and assessing its impacts on the environment such as melting of glaciers and sea ice and sea level rise, Copernicus supports Europe’s climate change adaptation and mitigation policies in several sectors.
Insurance and Disaster Management
Copernicus supports public authorities in all phases of disaster management, from preparedness, prevention and disaster response, where it supports civil protection operations with products such as disaster maps for example, to the recovery phase, where it helps to monitor the medium- and long-term impacts on the environment, human safety and the economy.
Transport
Copernicus provides numerous solutions to transport and transport safety issues, such as information on currents to support ship routing services and on environmental hazards, such as volcanic eruptions or the presence of sea ice, which can disrupt aviation and marine transport. Completed by the European positioning systems, Galileo and EGNOS, Copernicus is allowing the development of transport applications.
Urban Planning